Believe it or not, audio cables have a long history. In 1881, Alexander Graham Bell invented the first twisted conductor cables, with the goal of eliminating crosstalk. What is this? It’s a telecommunications term that means that between two circuits, parts of the signals in one circuit (the disturbing circuit) appear in the other (the disturbed circuit). In other words, Bell created his cables to eliminate the interference and noise that occurred with early electrically conducting cables.
Many years later, in the 1980s, an international standard for cables was created with the participation of the AES (Audio Engineering Society) and the EBU (European Broadcasting Union), among other telecommunications organizations.
Today we have analog cables and digital cables . The difference is that the former transmit information through electrical current, while the latter transmit information through a binary string (ones and zeros).
En este artículo nos enfocaremos en darte la información básica sobre los cables analógicos, comenzando por mencionar que este tipo de producto transporta una señal eléctricamente exacta a una señal sonora, de manera que dicha señal analógica es de naturaleza electromagnética.
Thus, the audio signal is transported along a line that forms an electrical circuit, that is, a round trip, from a point of origin to a point of arrival and return. The cable is part of that line.
Existen dos presentaciones de cables analógicos:
1) Balanced Cables
2) Unbalanced Cables
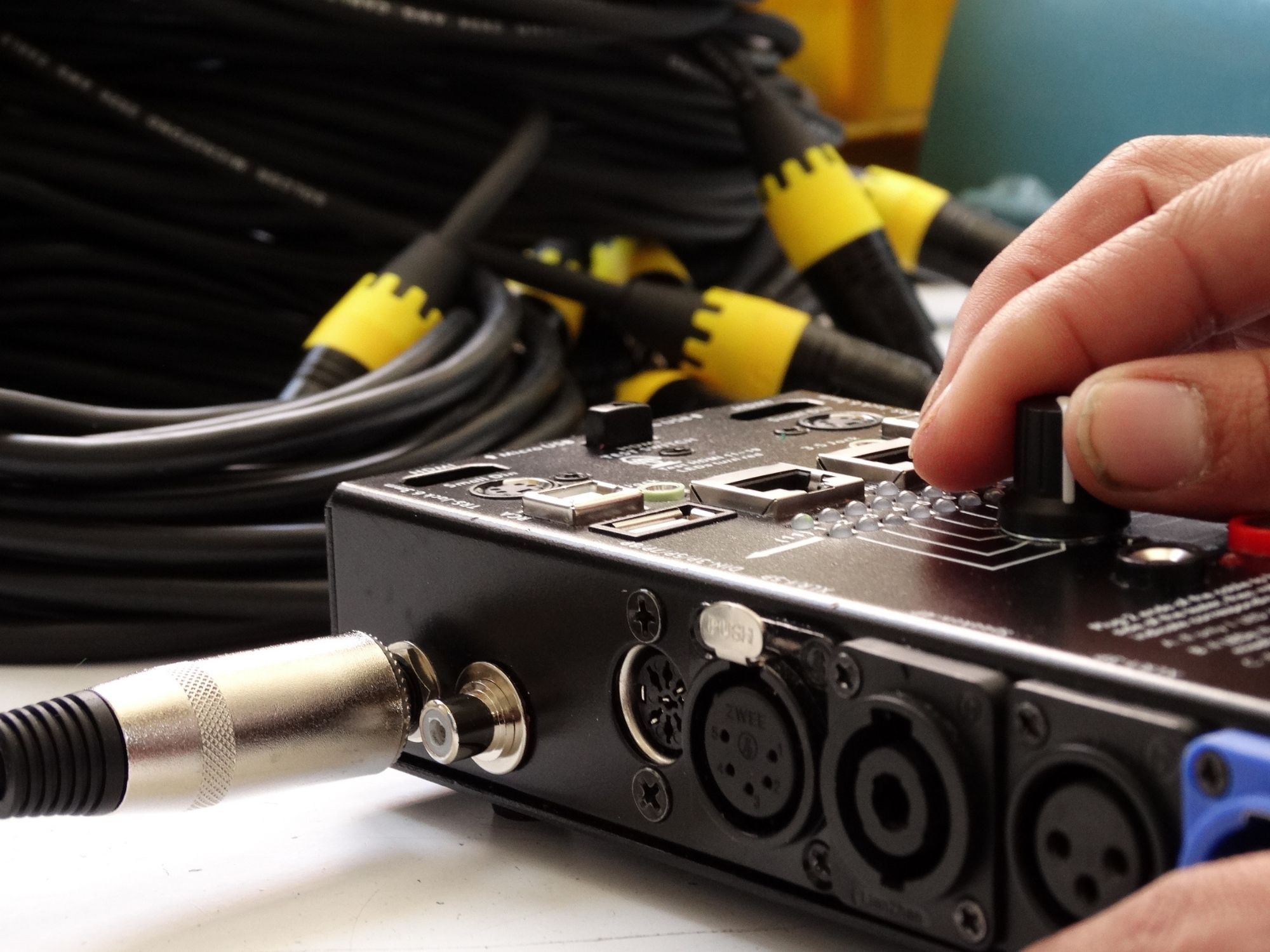
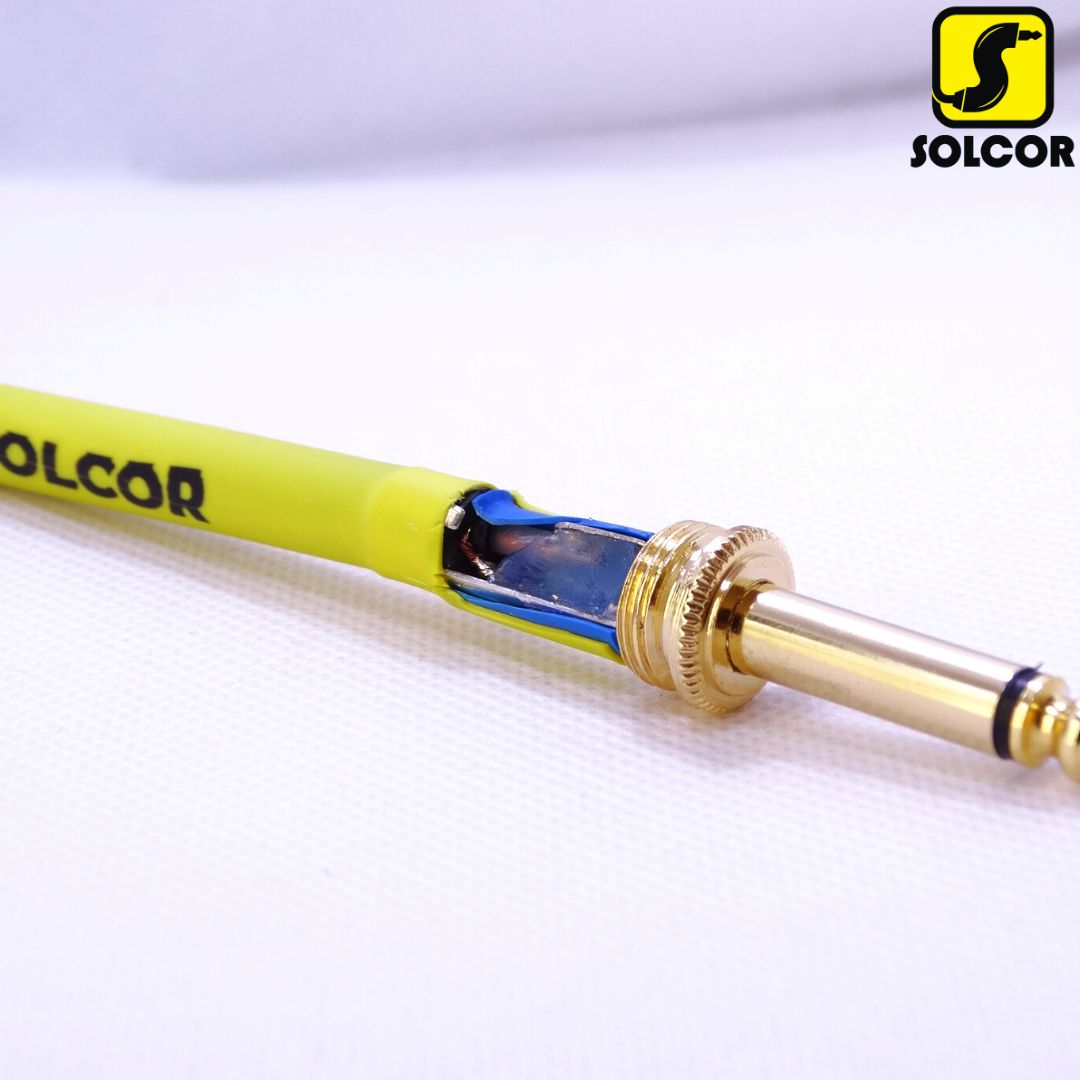
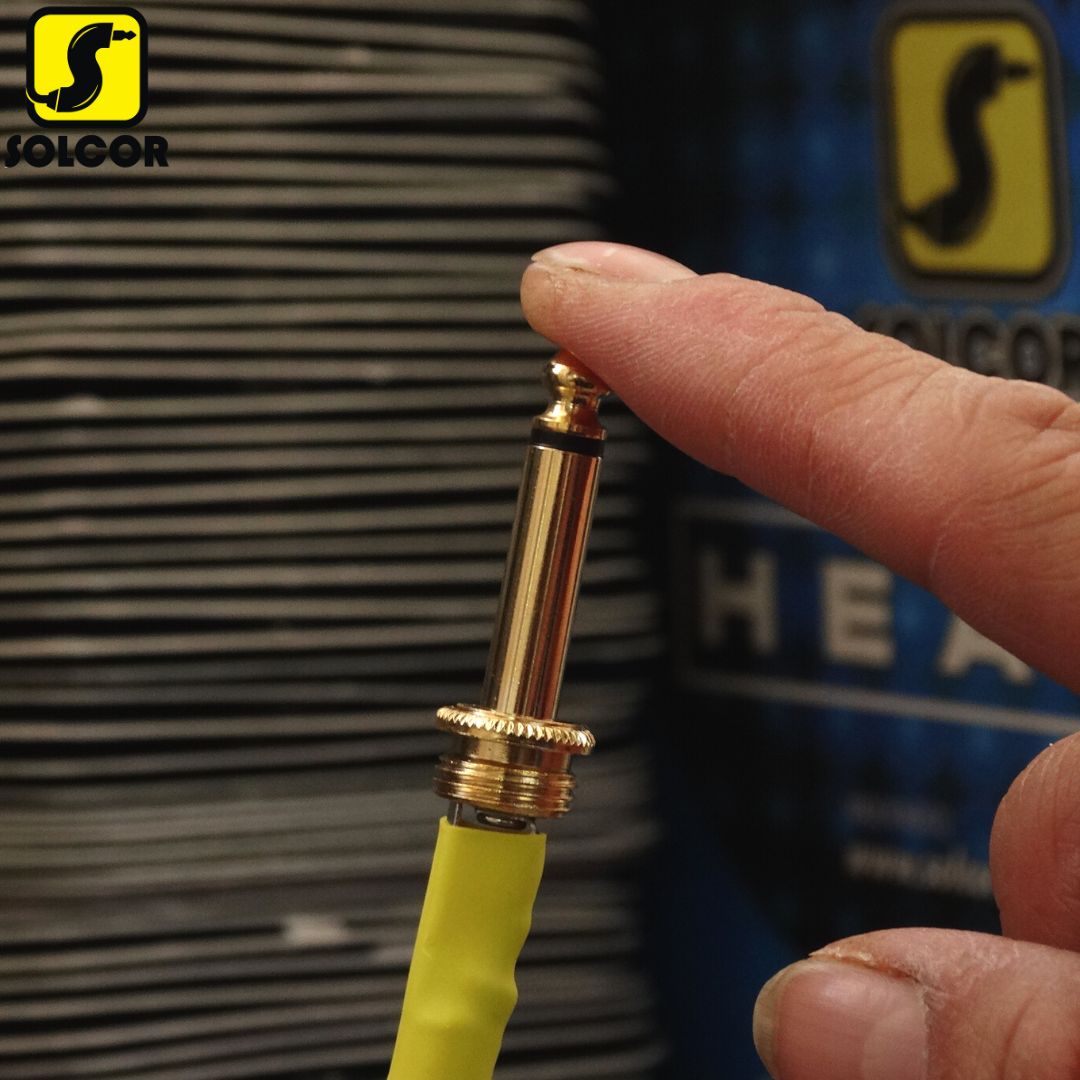
What’s the difference? Balanced cables have three wires: one positive, one negative, and one ground; this prevents interference such as radio frequencies or noise from nearby electronic equipment from entering.
Los cables no balanceados solo tienen 2 alambres: uno positivo y uno negativo, lo que en muchos casos permite la entrada de varios tipos de interferencia.
Both types of cables are used to transmit audio signals from microphones, instruments, and the connection lines between them.
Don’t miss the next posts of SOLCOR , to stay informed from the most basic to the most specialized in the world of wiring for musical instruments .